
INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
(ECON 2404)This undergraduate course is based on Hal Varian's textbook (9th Edition) with added rigor by means of formal definitions and mathematical proofs. Some materials are borrowed from Osborn & Rubinstein's Models in Microeconomic Theory. If you run into access issues, please check this or contact me.
PART I
Introduction
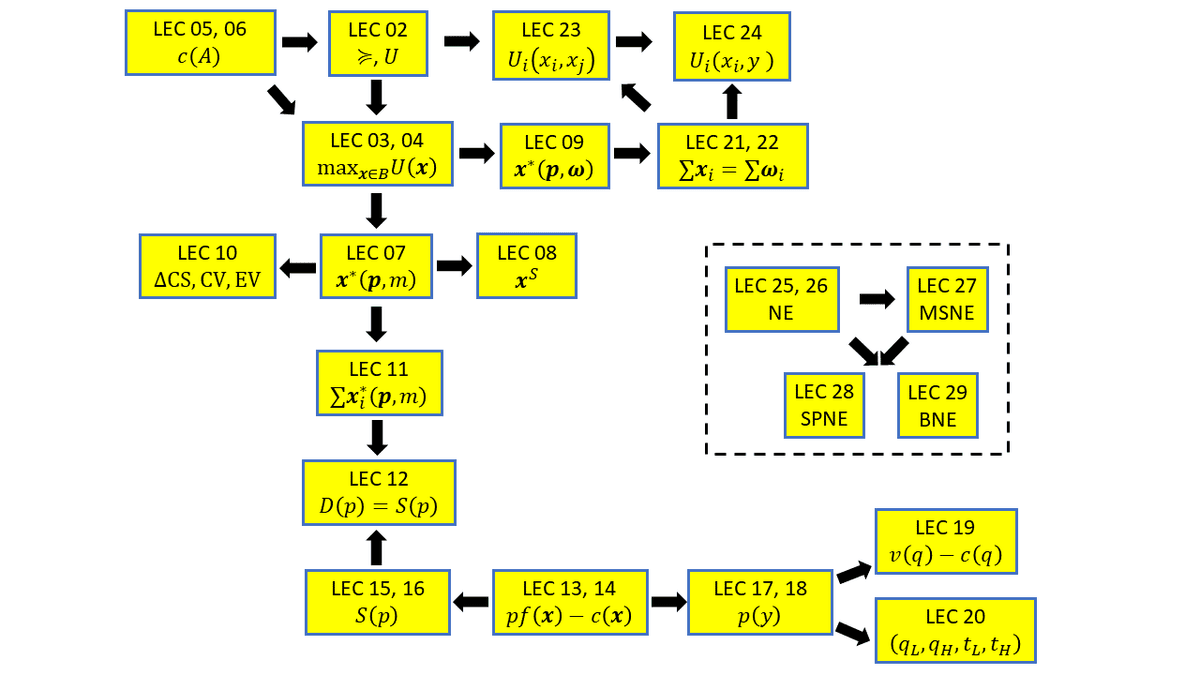
about this course; first look at rationality, equilibrium and efficiency; in-class illustration of a market (CH 1)
Decision Theory
preference relations; utility representation theorem; cardinal vs ordinal utility; convex preferences (CH 3 & 4)
utility maximization under budget constraints; indifference curves; marginal rate of substitutions and price ratio (CH 2 & 5)
Lagrange method; well-behaved preferences and sufficient conditions; various examples (CH 5)
weak/strong axiom of revealed preferences; rationalizable datasets; representation theorems (CH 7)
system of prices and income; SARP and well-behaved preferences; checking weak/strong axiom; applications (CH 7)
Demand Analysis
Marshallian demand; price/income changes; Giffen goods; Engle curves; homothetic preferences (CH 6)
Slutsky's decomposition; income effects and substitution effects (CH 8)
buying and selling; ordinary income effect; endowment income effect; application in labor supply (CH 9)
visualizing consumer surplus; quasi-linear utility and dollar measure; compensating and equivalent variations (CH 14)
Partial Equilibrium
aggregate demand; representative agent; weak axiom; elasticities; revenue maximization (CH 15)
demand, supply, and equilibrium; taxation and subsidy; tax incidence; implications on welfare (CH 16)
PART II
Neoclassical Firms
production; marginal rate of technical substitution; return-to-scale; marginal revenue and marginal cost (CH 19 & 20)
Cost minimization; Lagrange method; average cost; marginal cost; long-run/short-run; variable/fixed cost (CH 21 & 22)
supply curve; long-run vs short-run profit; producer surplus (CH 23)
cost data and supply curve; industry/aggregate supply; long-run equilibrium; free entry; economic profit and economic rent (CH 24)
Market Power
price as a decision variable; market power; tatal surplus; efficient output; markup; dead-weight loss (CH 25)
markup, elasticities, and Lerner index; price control and price ceiling; marginal revenue product; factors supply (CH 25 & 27)
non-linear pricing; 1st degree price discrimination; surplus extraction; 3rd degree price discrimination; two-part tariffs (CH 26)
2nd degree price discrimination; Riley Maskin screening, menu design and incentive compatibility (CH 26)
General Equilibrium
Walras law; excess demand; market clearing; Walrasian equilibrium; Edgeworth box; existence theorem (CH 32)
Pareto-optimality; 1st & 2nd Welfare Theorems; Edgeworth box, contract curve, core allocations (CH 32)
externalities; property rights & Coase's conjecture; production externalities; tragedy of the commons (CH 35)
Pareto-optimal level of public goods; uniqueness under quasi-linear preferences; provision decisions (CH 37)
Game Theory
pure strategies; simultaneous move; Nash equilibrium; Nash bargaining; dominant strategy equilibrium (CH 29 & 28)
Cournot competition; Bertrand competition; Vickrey (second-price) auction (CH 29 & 28)
randomization; expected utility; mixed strategy NE; best response correspondences; existence of NE; symmetric equilibrium (CH 30)
complete contingent plan; backward induction; subgame perfect NE; non-credible threat; various applications (CH 29 & 30 & 28 & 27)
types; adverse selection; Akerlof market for lemons; moral hazard; work or shirk; signaling; Spence education model (CH 38)
Other Materials
Blue Book
(pin on Canvas)
Black Book
(pin on Canvas)
FAQs
Office hour
I have year-round office hour (even when I am not teaching). Please check my homepage: www.xzlim.com
Letter for PhD applications
In a typical year, I write letters for at most 3 students who apply to top 30 econ PhD programs, usually the best students who took my class and continued to interact with me
Letter for Master's or job applications
You automatically qualify for a letter if you attend class and receive a grade of 80 (Fall 2023) / 90 (Fall 2022, 2024 and after). The degree of personalization depends on how well I know you
Auditing the class
Antai majors/minors are welcomed. Non-Antai students should seek permission via email (up to 20% of class capacity)
Other intermediate micro classes
Exams are the same (barring language differences), but my lectures emphasize rigorous introduction of concepts and the use of mathematical proofs. Please choose wisely!
TAs
LU Feifei (2021), FENG Xuechun (2022), QI Rui (2022), LIU Xingwen (2023), SU Tan (2023), GUO Li (2024), JIANG Xuehan (2024), LIU Mengxi (2024), LIU Yun (2024), SU Tan (2024), CHEN Zixiang (2025), LI Shaoyang (2025), WANG Yichen (2025), ZHANG Yili (2025), DONG Ruining (2026)
References
(1) Hal R. Varian. Intermediate Microeconomics: A Modern Approach (9th Edition). W. W. Norton & Company, 2014. (2, a.k.a "Blue Book") 钟根元, 陈志洪. 中级微观经济学学习指南(第四版). 上海交通大学出版社, 2012. (3, a.k.a. "Black Book") 钟根元, 陈志洪. 中级微观经济学. 上海交通大学出版社, 2020. (4) Andreu Mas-Colell, Michael Dennis Whinston, and Jerry R. Green. Microeconomic Theory. Oxford University Press, 1995. (5) Martin J. Osborne and Ariel Rubinstein, Models in Microeconomic Theory. Open Book Publishers, 2020.

